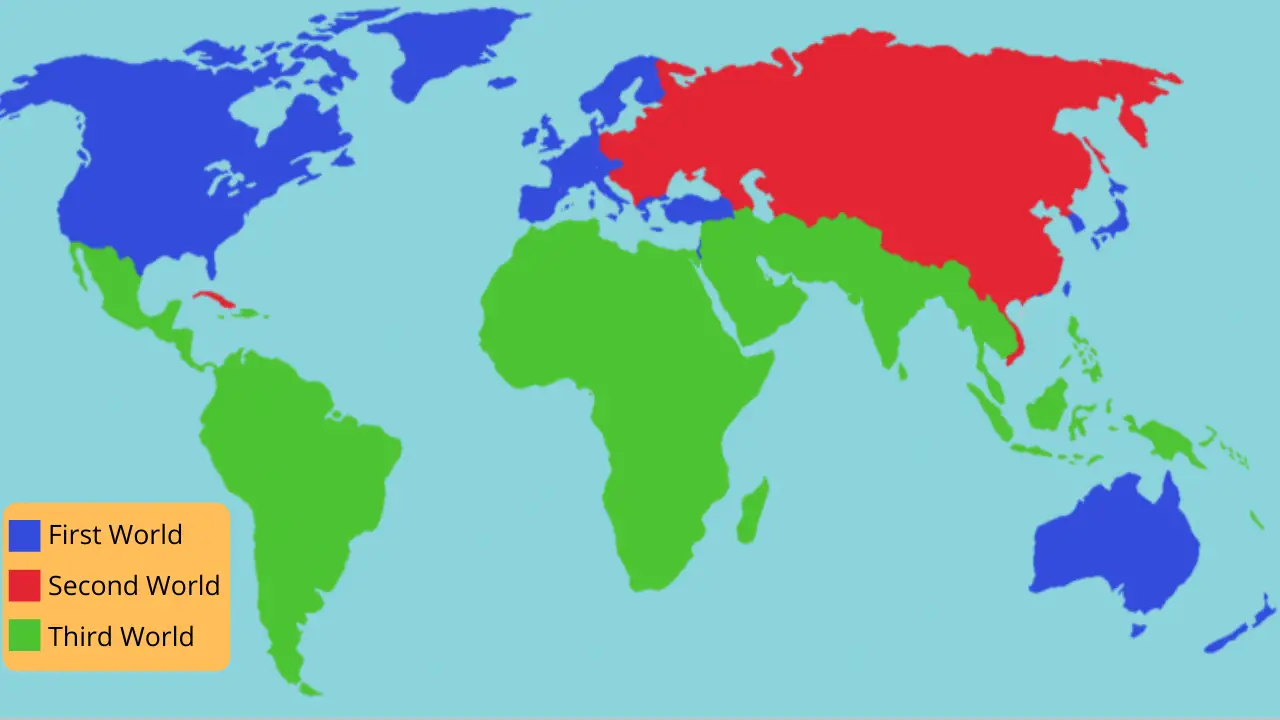
What are first-world, second-world, and third-world countries? The terms were coined during the Cold War to distinguish developed nations from developing ones. It is important to know what these 3 classifications mean so you can understand how they apply to your country.
What are first-world, second-world, and third-world countries?
- First World Countries are those with high standards of living and stable economies. They have a strong currency, high economic power, low inflation rates, and access to education for all citizens. These countries are wealthy with high-quality infrastructure, abundant natural resources, and a strong national defense system. Examples include the United States, Canada, Australia, Germany, and France.
- Second World Countries refer to the former communist-socialist countries. They also have stable economies, and developed infrastructures, but are less industrialized. These countries may lack some of the benefits that other first-world countries enjoy like universal healthcare or free education at public schools. Examples might be China or Russia.
- Third World Countries are those which have low levels of development and low living standards. These countries may lack the stability that first or second-world countries enjoy. They are characterized by lower levels of infrastructure, fewer natural resources, and a less-developed production base. They have very high unemployment rates and large gaps in income distribution among different social classes. Examples include Brazil or India.
There is also the term “Fourth World countries” that include cultural entities or ethnic groups of indigenous peoples that have never been incorporated as part of a nation-state, including some indigenous tribal groups.